Exercise physiology could be referred to as the study of the human body’s mechanisms involved in an exercise response to describe how muscles, the heart, and lungs respond to exercise. Understanding such provides a basis for improving fitness, performance, and health. On the basis of theory and application of the exercise physiology to fitness and performance, better training plans could be designed to get stronger, faster, and healthier.
“Exercising is much more than simply moving. It’s about understanding how our bodies work and how we can strengthen them. By studying the theory of exercise physiology and bringing that knowledge into practice in both fitness and performance, we learn how to train smarter, recover better, and fuel our bodies better. This will help us reach our goals and live healthier.”
Understanding Exercise Physiology
1. Key Concepts in Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance are studies of how the body functions during exercise. Understanding what happens when we move actually involves many changes that our body takes on when in exercise. Muscles get to work harder, the heart, and lungs too. This helps the body get stronger with time.
We temporarily stress our body by the act of exercise. The body subsequently adapts to those changes. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance enhance the body’s response to stress, and we can run longer or lift heavier weights or go faster. Better health and strength are the ultimate result of a long-term adaptation of exercise physiology.
Moreover, Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance can help explain how we can prevent getting hurt. It makes us become aware of the best ways in moving our bodies and shows how to deploy our muscles correctly. When we do exercises correctly, we lower the risk of injury.
There are many types of exercises, each of them influencing the body differently. Running helps the heart, weight-lifting helps muscles, and stretching helps the body move easily. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance help us understand how each type of exercise works inside the body.
Those studying the exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance take note of several things.
2. Body Systems Involved in Exercise
Many parts of the body apply to exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance. There are several systems in the human body that coordinate with each other. Each system of the body has a specific function. Let’s have a closer look at three systems of our body that help us when we exercise.
How Exercise Affects Fitness Levels?
Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance keep your body fit and fine. It enhances your heart, muscles, and movement. Here’s how exercise can affect your fitness:
1. Cardiovascular Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular exercises have been beneficial for your heart. This exercise makes your heart stronger and promotes blood flow.
- Strengthens the heart muscles: Some cardio exercises, like running, walking, or swimming are highly recommended because, according to CSM Fitness California, they force your heart to pump more blood. After some time, it will strengthen your heart; a strong heart is capable of pumping more blood in one stroke.
- Decreasing blood pressure: One of the most important things that regular motion can help you achieve is a decrease in blood pressure. This happens because the heart is stronger and, therefore, will not have to work as much. The theory of exercise physiology and application to fitness and performance also keeps your blood pressure at a low and healthy level.
- Improving endurance: The theory of physiology exercise and application to fitness and performance makes the body adapt to doing more work. Increased volumes of blood reaching the heart means oxygen supply to the entire body is increased. This then enables one to work out for longer periods without easily getting worn out.
- Preventing cardiovascular disease: Cardio exercises decrease the chances of heart-related conditions. It keeps the heart healthy by improving the flow and elasticity of the blood vessels.
If you want a healthy heart, try doing exercises that make you breathe faster. These exercises are good for your heart and help your body stay fit. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance is key to understanding these benefits.
2. Strength and Muscle Development through Resistance Training
Resistance training makes your muscles stronger. This helps you move better and carry heavy things more easily.
- Building muscle strength: Lifting weights or doing exercises like push-ups and squats can make your muscles bigger and stronger. When you challenge your muscles, they grow over time. Stronger muscles help you do tasks like lifting heavy objects with ease. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance explains how these changes occur.
- Supporting bone health: Strong muscles protect your bones. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance helps build muscle around your bones, making them stronger. This lowers the risk of injury and keeps your bones healthy as you age.
- Improving posture: Strong muscles support your body. They help keep your back, shoulders, and neck in a good position. This prevents slouching and back pain. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performancehighlights the importance of posture in overall health.
- Preventing muscle loss: As you get older, your muscles can get weaker. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance helps prevent muscle loss. This keeps your muscles strong and healthy as you age.
To build muscle, try doing strength exercises. These exercises help your muscles grow and keep your bones strong. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance provides the foundation for these practices.
Principles of Exercise Physiology in Performance Enhancement
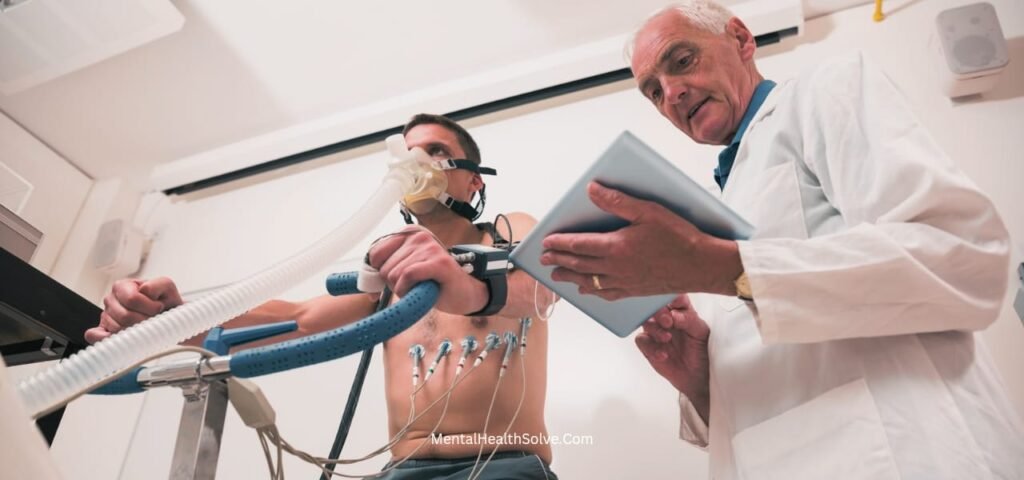
Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance helps athletes perform better. It shows how the body works during exercise and how it can improve. Here’s how it helps in performance:
1. Adaptation and Recovery Phases
When we exercise, the body changes to handle more work. This is called adaptation.
- Adaptation: The body gets stronger when we exercise. Muscles grow, and the heart pumps better. Over time, the body becomes better at handling exercise. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance explains these adaptive processes.
- Recovery: After exercise, the body needs rest. This is called recovery. Rest is important because it helps muscles repair and grow. Without recovery, the body can get tired and hurt. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance highlights the importance of recovery for long-term performance.
To get stronger and faster, athletes need both hard work and rest. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance guides athletes in balancing these two essential components.
2. Role of Energy Systems in Athletic Performance
The body uses energy to move. It has three main energy systems that help in different activities.
- Aerobic system: This system works during long exercises like running. It uses oxygen to make energy. This system helps athletes run or bike for a long time. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance covers the details of the aerobic system.
- Anaerobic system: This system helps with short, fast exercises like sprinting. It doesn’t need oxygen and gives quick energy. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance explains how the anaerobic system supports short bursts of activity.
- ATP-PC system: This is the fastest energy system. It helps with very short bursts, like jumping or lifting heavy weights. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance outlines the role of the ATP-PC system in explosive movements.
Each system plays a role in sports. Knowing how they work helps athletes train better. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance provides a deeper understanding of these energy systems.
3. Importance of Nutrition in Performance
Nutrition is key to good performance. The body needs food for energy, growth, and repair.
- Carbohydrates: These give quick energy. Athletes eat carbs before games or races to stay energized. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance shows how carbs fuel performance.
- Proteins: Protein helps muscles grow. After exercise, protein helps muscles repair and get stronger. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance explains the role of protein in muscle recovery.
- Fats: Fats give long-lasting energy. They help athletes during long activities, like running a marathon. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance covers the importance of fats in endurance sports.
Eating the right foods helps athletes perform at their best. Exercise physiology theory and application to fitness and performance ensures that nutrition strategies are optimized for peak performance.
FAQs
1. What is exercise physiology?
Exercise physiology studies how the body responds to physical activity.
2. How does exercise improve fitness?
It strengthens the heart, muscles, and bones.
3. Can exercise help with chronic diseases?
Yes, it helps manage and prevent many conditions.
4. What is the role of nutrition in performance?
Proper nutrition fuels the body and boosts recovery.
Final Thoughts:
Exercise physiology helps us understand how the body works during exercise. It shows how to train, recover, and eat right for better fitness and performance. By using this knowledge, we can get stronger, healthier, and improve in sports or everyday activities.

