
Separation anxiety disorder is a particular type of anxiety disorder. It triggers intense anxiety and fear related to being apart from a close attachment person. This goes beyond normal concerns about a loved one; it leads to significant distress and disrupts daily life. In adults, symptoms persist for at least six months, while in children, they last for a minimum of four weeks.
This goes beyond normal concerns about a loved one; it leads to significant distress and disrupts daily life. In adults, symptoms persist for at least 6 months, while in children, they last for a minimum of 4 weeks. Individuals may also experience physical signs of separation anxiety, like headaches and nausea. In this blog, I will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for separation anxiety.
What Is Separation Anxiety?
Separation anxiety is a mental health issue that can affect both children and adults. It leads to intense anxiety or fear when someone is separated from a close attachment person or even when they anticipate such a separation. This anxiety and fear are often disproportionate to the actual situation and are not typical for the person’s developmental stage.
For children, the attachment figure is generally a parent, but it can also be a grandparent or another caregiver whom they have shared a close bond with. In adults, the anxiety often revolves around their partner or child. You might recognize “separation anxiety” as something that infants experience when their primary caregiver leaves them.
This is because separation anxiety is a typical part of development for infants as they start to explore the world around them. Most children outgrow this phase by the time they reach three years old. However, some older children continue to experience separation anxiety beyond this developmental stage.
That is when healthcare professionals may diagnose them with separation anxiety disorder. Adults can also show symptoms, regardless of whether or not they have separation anxiety as children. This disorder can disrupt daily life significantly. Children might refuse to attend school, while adults might struggle to concentrate or miss work.
The good news is that it does not have to stay this way. If you suspect that you or someone you care about may have a separation anxiety disorder, reach out to a healthcare provider. They can discuss your concerns and, if needed, suggest treatment options like medication or therapy.
Separation Anxiety Disorder Symptoms
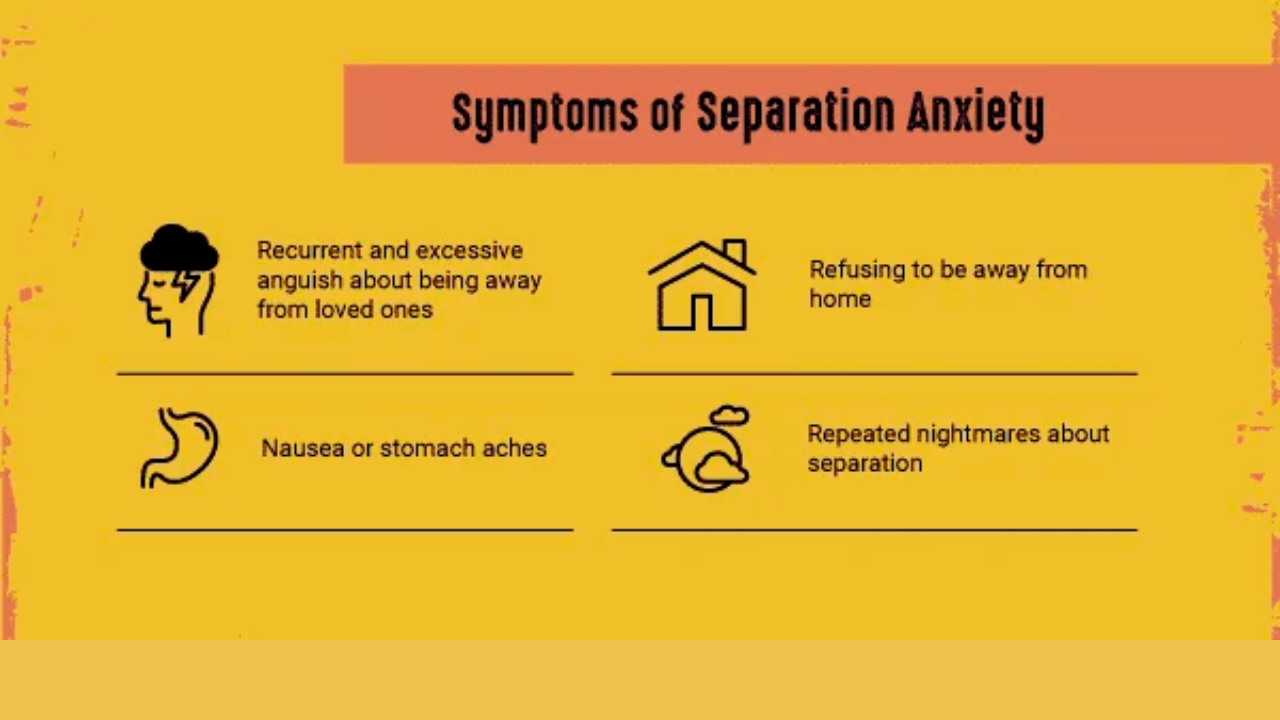
An individual with a separation anxiety disorder may experience 3 or more of the signs below:
- Worries that something terrible, such as injury or death, might happen to their attachment figure.
- They feel intense distress when they are away from an attachment person or even when they think about being separated.
- Fears that something bad could happen to them, such as being kidnapped or getting lost, which would lead to separation from their attachment figure.
- Experiences continuous nightmares about being detached from their attachment figure, which may involve disasters such as violence or fires.
- May refuse to go to places such as school or work or leave home because of their fear of being apart.
- They can have physical signs, such as nausea, stomachaches, vomiting, or headaches, when they are separated from their attachment figure or when they anticipate a separation.
- In adults and adolescents, these symptoms may include dizziness or heart palpitations, though these are less common in younger children.
- Might refuse to go to sleep unless their attachment figure is present.
- They have a strong fear of being alone, even in different parts of the house, without their attachment figure close by.
How Can You Identify Separation Anxiety Disorder In Children?

Separation anxiety in babies can vary based on your child’s age. For instance, a preschooler may struggle to express their feelings verbally and might simply become upset. In contrast, an older child may share their nightmares or express their fears more clearly.
If you insist on a separation despite your child’s objections, they may seem sad or disengaged in their surrounding environment, such as at school. They might find it hard to focus on their schoolwork and show little interest in interacting with their classmates. Their teacher may notice these behaviors.
When away from home for multiple days, like at a camp, a kid with a separation anxiety disorder may experience intense homesickness and feel unhappy until they can return home. In addition, this child might display anger or even aggression toward anyone they believe is preventing them from being with you.
How Can You Identify Separation Anxiety Disorder In Adults?
Health professionals once viewed separation anxiety as a disorder primarily affecting children, with symptoms typically appearing before the age of 18. Till the DSM-4 edition (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edition), separation anxiety was not allowed for new diagnoses in adults. However, the latest edition, DSM-5, has changed this guideline.
Separation anxiety in adults often revolves around being apart from a romantic partner, a spouse, or children. They may worry that something harmful could occur to their loved ones while they are apart. These feelings can lead to substantial distress, impacting social interactions, work, or academic performance.
Sometimes, people might label an adult diagnosed with separation anxiety disorder as overly protective or controlling. However, these behaviors often reflect the adult’s way of coping with their fears about separation.
Causes of Separation Anxiety Disorder
Researchers are still trying to pinpoint the exact causes of separation anxiety, but they think it likely originates from a mix of environmental and genetic factors. For instance, a person may inherit a genetic mutation that influences how specific brain chemicals function. However, genetics alone may not be sufficient to trigger the disorder.
Environmental factors, such as significant life changes or negative childhood experiences, probably play a crucial role as well. These factors can lead to epigenetic changes, which are modifications to the chemicals tied to your genes that impact how those genes operate. For instance, some epigenetic changes may alter how your body’s cells interpret the genes responsible for managing stress responses.
What Are The Treatment Options for Separation Anxiety Disorder?

Therapies
The primary treatment for this disorder is psychotherapy (talk therapy), particularly a type called cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). It helps individuals understand how their thoughts influence their behaviors. Other therapeutic options are given below:
- Family Therapy: This therapy focuses on improving relationships among family members and educating everybody about separation anxiety disorder.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): It assists individuals in finding a balance between accepting themselves and embracing change.
Medications
If talk therapy isn’t providing enough relief, you or your child might require medication. Your healthcare provider will discuss the specific type of medication that would be most effective and how long it may be necessary to take it.
Medications for Treating Separation Anxiety Disorder in Kids
Healthcare providers sometimes prescribe SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) to treat separation anxiety disorder in kids aged 6 and older. Some specific medications that may be recommended include:
- Paroxetine (Pexeva®, Paxil®)
- Sertraline (Zoloft®)
- Fluoxetine (Prozac®)
Possible side effects can include vomiting, insomnia, and changes in appetite. One significant concern with using SSRIs in children is the elevated risk of suicidal thoughts. Your child’s doctor will closely monitor them for any signs of suicidal ideation.
They will schedule regular follow-up appointments for your child, which may occur weekly during the first month. After that, visits will typically shift to every second week in the second month. They will also inform you about what to watch for at home. Feel free to discuss any concerns or questions with your child’s provider at any stage of this procedure, including before starting any medication.
Medications for Treating Separation Anxiety Disorder in Adults
Your healthcare provider might prescribe antidepressants such as SSRIs or anti-anxiety medications such as benzodiazepines. They will explain the potential side effects and risks associated with the particular medications you are taking. For instance, benzodiazepines can lead to dependence.
SSRIs might raise the risk of suicidal behaviors or thoughts, particularly when you first begin treatment. Every medication has its own set of risks and benefits. You and your healthcare professional can collaborate to determine the best treatments for your needs.
The Bottom Line
Although adult separation anxiety is less common than in children, it’s still possible for adults to experience this condition. The anxiety can become so overwhelming that it interferes with daily life, making it hard for someone to cope with the fear of being apart from someone they care about.
Children with separation anxiety disorder face a similar struggle. Their worries and fears can significantly impact their ability to concentrate in school or enjoy time with friends. Regardless of when it starts, separation anxiety disorder can interrupt everyday life.
If you witness signs of this disorder in yourself or your kid, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. They are equipped to diagnose and treat this health issue.
