
Generalized anxiety disorder is a mental health issue where you frequently feel extremely anxious about a variety of things. Diagnosing generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) can be tricky. Many people associate panic attacks with anxiety disorders. However, GAD is different because it typically doesn’t involve panic attacks.
Due to this misunderstanding, someone without panic attacks might think they’re just worrying a lot. This continuous worry might be downplayed or overlooked, leading to a lack of proper diagnosis and treatment. In this article, I will cover everything you need to know about GAD.
What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?

Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is characterized by excessive worry that feels difficult to control. If you have GAD, you often anticipate disaster and find it hard to stop worrying about various aspects of life, such as family, health, finances, school, or work. Healthcare professionals diagnose GAD when this worrying occurs most days for at least six months.
It’s one of the most prevalent mental health conditions in the United States. You might have grown accustomed to worrying, believing it is just part of who you are. While it’s normal to occasionally worry about things like money, family, or health, constantly expecting the worst can hinder your ability to live a fulfilling life.
GAD typically develops gradually, often starting in childhood or adolescence. However, it can also start in adulthood. It is more frequently diagnosed in individuals assigned as females at birth and tends to run in families. If you experience a generalized anxiety disorder, you might also struggle with another mental health issue, like depression.
What Causes Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
Researchers aren’t entirely sure what causes Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), but they believe it is a complex mix of environmental, genetic, and biological factors. If you have a close family member, like a parent or sibling, with GAD, your chances of developing it are higher.
One of the most common causes of generalized anxiety disorder is struggling to manage internal stress. However, it is unclear why some people develop it while others don’t. Studies indicate that the brain’s regions responsible for fear and anxiety are impacted by this mental health condition.
In some cases, GAD’s symptoms can emerge as an adverse effect of substance abuse or medication. Furthermore, it can be associated with medical conditions, like hyperthyroidism, that elevate hormone levels, making the body more reactive. In addition, researchers have identified the following generalized anxiety disorder causes:
- Dealing with a chronic illness.
- Going through a traumatic event.
- Suffering from child abuse.
- Living in a high-stress environment.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Symptoms
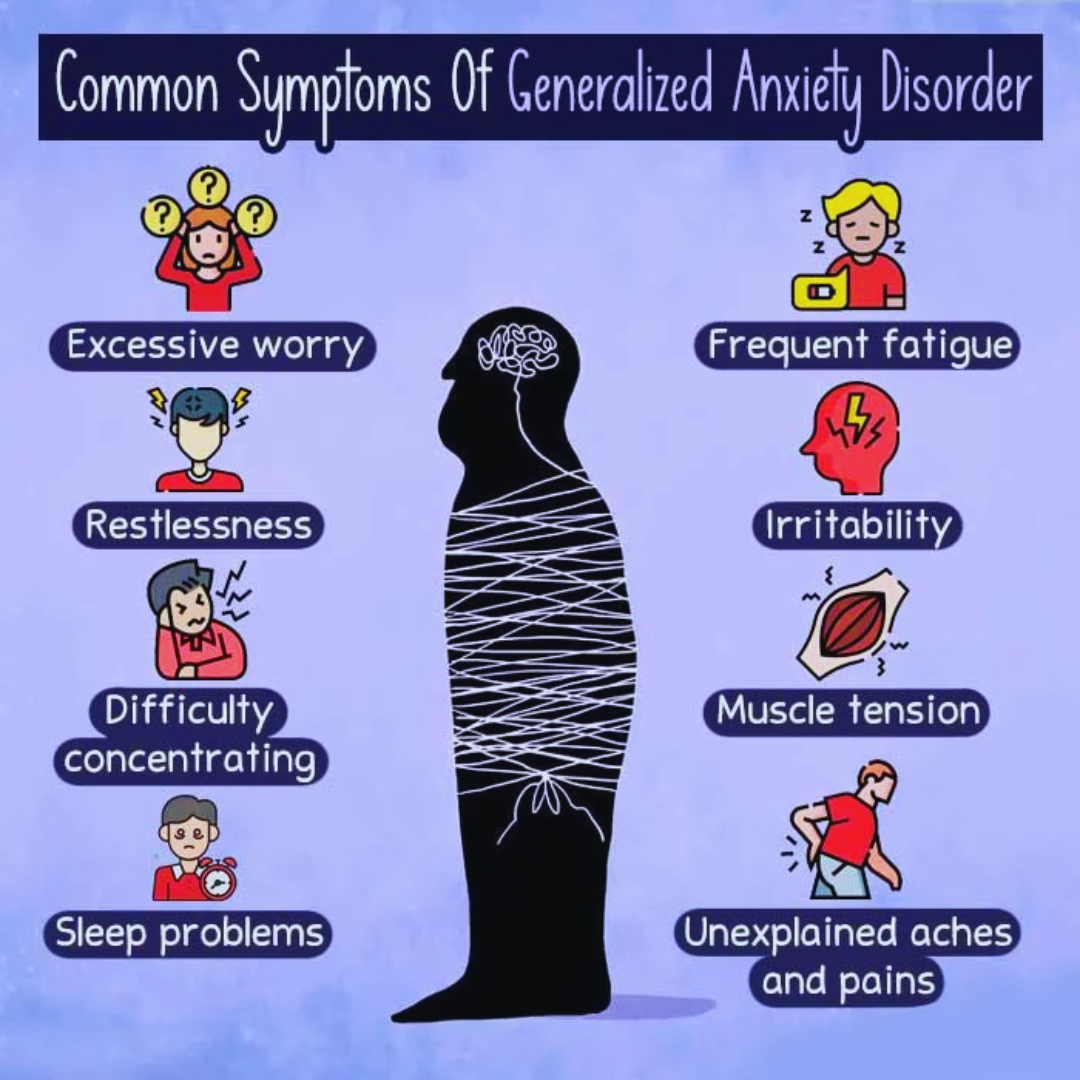
One of the most common symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder is constant and overwhelming worry about everyday matters. This ongoing sense of fear or anxiety disrupts your daily life. Individuals with GAD struggle to manage their anxious thoughts or nervousness and are often aware that their level of worry is excessive.
The intensity of GAD symptoms can vary over time, typically worsening during stressful periods. This relentless tension and worry can also bring about physical symptoms. Some generalized anxiety disorder signs and symptoms are:
- Getting tired quickly.
- Feeling restless.
- Feeling muscle tension.
- Experiencing dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Having heart palpitations.
- Struggling to concentrate.
- Feeling irritated or on edge.
- Having a low mood or feeling depressed.
- Having trouble falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Experiencing shortness of breath.
- Suffering from stomachaches, muscle aches, headaches, or unexplained pains.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Diagnosis
Mental health experts and medical care providers rely on the criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (DSP-5), to diagnose generalized anxiety disorder. This criteria are given below:
- Experiencing excessive worry and anxiety for a minimum of six months.
- The anxiety causes substantial distress or disrupts daily life.
- Struggling to control the worrying.
- The anxiety is not linked to a physical cause, like substance use or thyroid problems.
The anxiety is also accompanied by three or more of the below signs for a minimum of 6 months:
- Having trouble concentrating.
- Feeling restless or on edge.
- Facing sleep difficulties.
- Feeling irritable.
- Getting easily tired.
- Experiencing muscle tension.
If you suspect that you or your kid might have GAD, it is crucial to consult a medical care provider or a mental health expert, like a psychologist. A medical care provider will conduct a physical examination and might order a few tests to rule out any substances or physical conditions causing your signs. These tests could include:
- Blood glucose test.
- Thyroid blood tests.
- Toxicology screen (drug test).
- Echocardiogram (heart test).
Treatment for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
GAD is typically treated with talk therapy (psychotherapy), medication, or a combination of both.
Talk Therapy
Talk therapy is often referred to as psychotherapy. It encompasses various treatment methods designed to help individuals recognize and alter unhealthy behaviors, emotions, and thoughts. Talk therapy is conducted by a licensed, trained mental health expert, like a psychiatrist or psychologist.
It offers guidance, support, and education to you and your family, helping you function better and improve your health. Mental health experts frequently use cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to address GAD particularly.
In CBT, your therapist will help you closely examine your emotions and thoughts. With CBT, you can forget negative or anxious thoughts and behaviors and start embracing healthier ways of thinking and acting.
Medications
Your psychiatrist or healthcare provider might prescribe medication to treat generalized anxiety disorder. Here are some types of medications they might consider:
Anti-anxiety Medications: Benzodiazepines, which are sedatives, can help control severe GAD. They work effectively to reduce anxiety quickly, but some people may develop a tolerance, requiring higher doses to obtain the same effect. Due to this, your healthcare provider might prescribe them for short-term use if needed. Another option is Buspirone, an anti-anxiety medication that can assist in treating GAD. However, it takes 3-4 weeks to reach full effectiveness.
Antidepressants: Healthcare professionals often prescribe SNRIs (serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) and SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) to treat depression, but these can also alleviate GAD symptoms. They may take a few weeks to become effective.
Is It Possible to Prevent Generalized Anxiety Disorder?

It is impossible to predict exactly what might lead somebody to experience generalized anxiety disorder. However, there are some steps that you can take to lessen the impact of anxiety symptoms:
- Prioritize Problems In Your Life: Managing your energy and time wisely can help reduce anxiety.
- Seek Help Early: Like many mental health issues, anxiety can become more challenging to treat if you delay getting help.
- Avoid Using Unhealthy Substances: Nicotine, drugs, alcohol, and even caffeine can trigger or worsen anxiety. If you’re dependent on any of these, quitting might increase anxiety. If you find it difficult to quit on your own, consult your healthcare provider or join a support group or treatment program for assistance.
- Keep A Journal: Documenting your daily life can assist you and your healthcare provider in pinpointing stress triggers and identifying what helps you feel better.
Final Words
Generalized Anxiety Disorder involves excessive worrying that is difficult to manage. It’s important to remember that GAD is treatable, so you or your child don’t need to suffer in silence. Treatment options, especially self-help strategies, psychotherapy, or other therapies, can equip you with various techniques to handle anxiety. Medications are also available to help you.
With the right treatment, most people with generalized anxiety disorder experience significant relief from their symptoms. Since GAD can lead to other complications, it is crucial to keep it under control.
