
Sadness is a normal part of life. People often feel depressed or sad when they lose a loved one or face difficult situations in their lives, like a severe illness or divorce. These feelings generally don’t last long. However, if someone experiences deep and continuous sadness for a long time, they might have a mood disorder like clinical depression.
Some people experience this type of depression only once, while others may face it multiple times throughout their lives. Clinical depression can be very challenging to cope with and may lower your quality of life. It can negatively impact your relationships with other people, your sense of self-worth and your self-esteem.
Also, it may impact your work performance or even make it difficult to work at all. That is why it’s crucial to seek help if you’re dealing with clinical depression. Let’s take a closer look at this health condition.
What Is Clinical Depression?

Clinical depression, also called major depressive disorder (MDD), is more than just feeling down or upset for a few days. It involves a persistent low mood that can last for several weeks or even several months, with symptoms that are often severe and overwhelming.
This condition can significantly impact every part of your life. Clinical depression makes it hard to take care of yourself or handle your daily tasks. Simple activities such as dressing, getting out of bed, or bathing might feel impossible. You might feel isolated and as if depression has taken over every aspect of your life, turning each day into a challenge.
Major depressive disorder is one of the most prevalent mental health issues in the U.S. In 2021, studies show that over 8.3% of United States adults underwent a major depressive episode. While some people with clinical depression do not seek treatment, many individuals can learn to manage and cope with their symptoms through treatment.
Therapy, medications, and other approaches can effectively treat individuals with clinical depression and assist them in managing their symptoms. There are different subtypes of clinical depression. These include:
- Atypical depression
- Postpartum depression
- Seasonal affective disorder
- Prenatal depression
Individuals suffering from depression frequently have other mental health issues, including:
Clinical Depression Symptoms

Not everybody with depression will have similar signs, and the signs can vary depending on the kind of depression. However, someone suffering from major depressive disorder (MDD) might consistently experience some of the following symptoms:
- Restlessness
- Sadness or a lack of interest in activities they generally enjoy
- Hopelessness or a negative outlook
- Irritability
- A sense of emptiness
They might also experience the following signs of clinical depression:
- Changes in appetite or eating habits
- Tiredness
- Suicidal thoughts
- Headaches
- Withdrawal from others
- Digestive issues
Isolation - Sexual problems
- Substance use
- Challenges with school, work, or family duties
- Facing challenges with the duties of family life, school, or work
- Weight changes
- Trouble sleeping or sleeping a lot
- Risky behaviors
Signs in Teenagers

Parents should watch for certain symptoms of clinical depression in their teenagers, including:
- Withdrawing from friends and social activities
- Starting or increasing the use of substances like cigarettes or alcohol
- Displaying changes in behavior or more frequent behavioral issues
- Showing agitation and irritability
- Declining grades or poor school performance
- Experiencing sudden mood swings
Signs in Elderly Persons
Clinical depression signs in elderly persons share similar symptoms with other age groups and are often referred to as geriatric depression. It can lead to physical pain in elderly persons that isn’t linked to other medical issues. Nevertheless, it is important to check for other health conditions that might be causing symptoms similar to depression in elderly persons.
What Causes Clinical Depression?
Clinical depression is a complicated mental health issue, and researchers think that it doesn’t have just one cause. Instead, several factors can contribute to its development. Some of the clinical depression causes are:
- Age: As people age, the risk of depression can rise because of loneliness, brain changes, and other health issues.
- Personal or family history: If you or your family members have a history of mental health problems, your risk of depression may be higher. Genetics might play a role here.
- Personality traits: Traits such as self-criticism and perfectionism can increase the likelihood of clinical depression.
- Traumatic or distressing events: Situations like losing a loved one, ending a relationship, or losing a job can trigger depression.
- Significant life changes: Major changes in life or high-stress situations can lead to depression.
- Childhood abuse or neglect: Difficult experiences in childhood can make it hard to handle negative emotions, which might lead to depression.
- Gender: Women face a higher risk of clinical depression because of societal pressures, hormonal changes, and increased production of stress hormones.
- Physical health issues: Chronic illnesses or serious health problems can result in depressive symptoms.
Clinical Depression Treatment Options
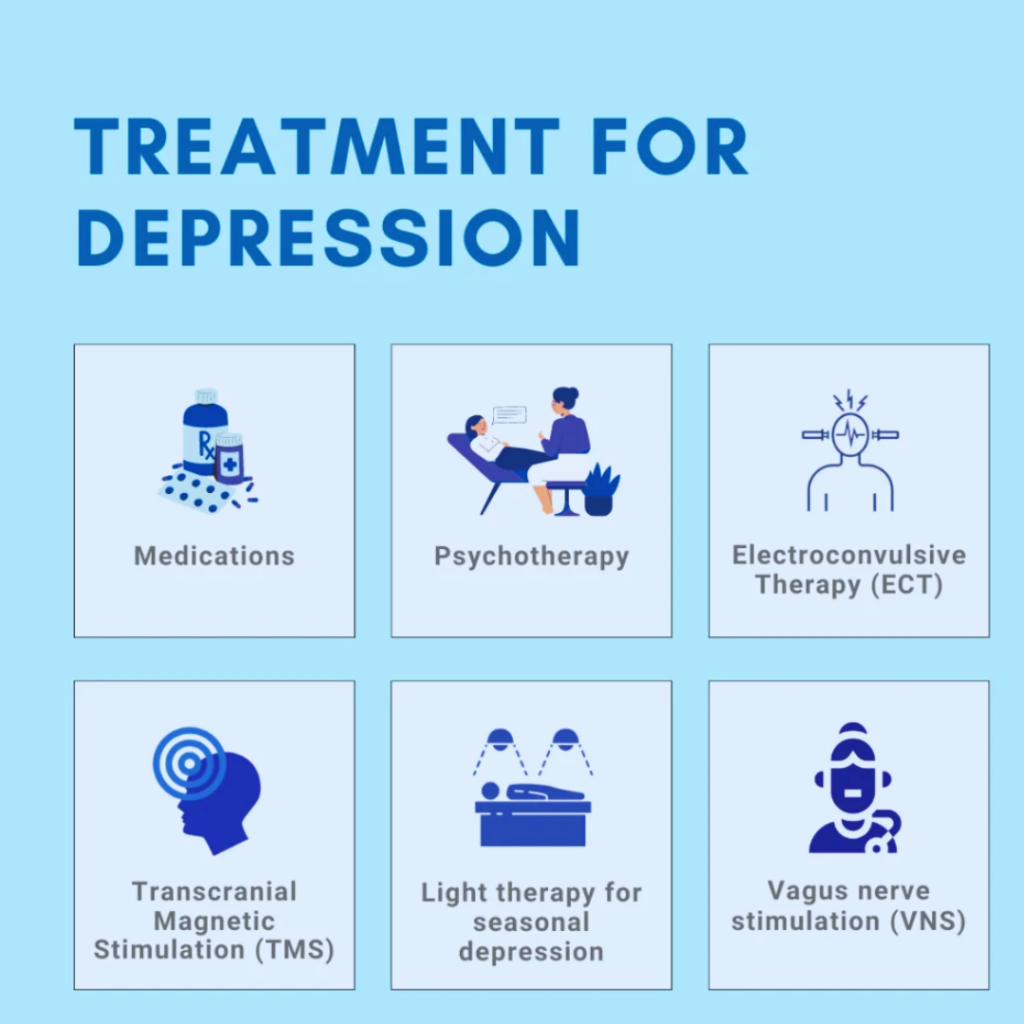
Treating clinical depression, or major depressive disorder, often involves using talk therapy (psychotherapy) and medications. Research indicates that combining these treatment options is more effective than using either one alone. Talk therapy involves sessions with a mental health expert, like a psychologist.
During these sessions, your psychotherapist helps you recognize and change negative thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Common types of therapy for clinical depression include interpersonal therapy (IPT) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). You might meet with your therapist weekly or every other week.
Antidepressant medications can help adjust the brain chemistry linked to depression. There are various types of antidepressants, and finding the right one for you might take time and require trying more than one medicine. These medications can have side effects, but they often lessen over time.
When it comes to severe clinical depression that doesn’t improve with other treatment options, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can be very effective. ECT involves sending a mild electric current via the brain to trigger a brief seizure. It is a safe procedure done under general anesthesia and is not painful.
Other stimulation therapies for depression that don’t respond to medication include:
- Ketamine and Esketamine treatments
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
- Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)
How long does it take for depression treatment to begin working?
You might start to notice some improvement in your signs within the first 1-2 weeks after beginning antidepressants. However, it can take 2-3 months to experience the full effects of the medication. If you don’t see any improvement after this period, consult your medical care provider. They might change the dosage or recommend a different antidepressant.
For psychotherapy, the time it takes to feel better can vary based on how severe the depression is. It might take a few weeks or longer to feel better, but many people see significant improvement after 10-15 sessions.
Final Thoughts
Clinical depression, also known as major depressive disorder (MDD), is a common mental health condition. It can affect anyone, even if there seems to be no clear reason for it. Although living with major depressive disorder can sometimes feel overwhelming, it is crucial to know that effective treatments are available. There is hope for recovery.
Following your treatment plan is crucial for improving your mental health. Make sure to attend every therapy session and every follow-up appointment with your mental health provider. Also, you need to continue taking your prescribed medications unless your mental health provider advises otherwise.
