
It is crucial to maintain a good level of fitness. However, understanding what physical fitness truly means can be challenging. Different aspects of physical health contribute to determining one’s fitness level. Fitness encompasses a range of attributes related to health and skills.
It is defined as having the capacity to perform daily activities energetically and attentively without excessive tiredness. Fitness also means having enough energy to enjoy leisure activities and handle unexpected situations. Specific tests can measure how well individuals possess these attributes. This article explores the major components of physical fitness.
What Is Physical Fitness?

Just as fine-tuning enhances an engine’s performance, physical fitness boosts our body’s capabilities. It helps us feel, look, and perform at our best. Fitness involves the efficient functioning of the muscles, heart, and lungs. Since our physical state impacts our mental abilities, being fit can improve mental sharpness and emotional balance.
Physical fitness is about how well your body systems work together to keep you healthy and efficiently handle daily tasks. Efficiency means completing everyday activities with minimal effort. A fit individual can manage household duties, tackle schoolwork, and still have sufficient energy for playing sports and enjoying other leisure activities.
A physically fit person can handle everyday challenges efficiently, like playing in a school band, raking leaves at the house, or stocking shelves at a job. They can also react well in emergencies, such as running to obtain help or assisting a friend in need.
You can improve your physical fitness through regular exercise and physical activity. The components of fitness are closely linked to better performance in physical activities, including taking part in sports.
What Are The 5 Components of Physical Fitness?

Achieving physical fitness relies on how effectively someone meets each aspect of being healthy. There are 5 components of physical fitness. They are:
- Cardiorespiratory fitness
- Muscular endurance
- Muscular strength
- Flexibility
- Body fat composition
Let’s check out each of the components of physical fitness in detail.
- Cardiorespiratory Fitness
Cardiorespiratory fitness measures how efficiently the body delivers energy during physical activities through the body’s respiratory and circulatory systems. To boost cardiorespiratory endurance, engage in activities that keep your heart rate elevated for extended periods. These activities include:
- Cycling
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Jogging
People who consistently participate in these exercises are more likely to achieve better cardiorespiratory fitness. It’s crucial to start slowly and gradually raise the intensity of the exercise over time.
Exercise increases cardiorespiratory fitness in several ways. For instance, the heart becomes stronger, allowing it to pump more blood with each heartbeat. In addition, new small arteries develop within muscle tissue, improving blood delivery to active muscles when needed.
How Does Exercise Impact Heart Health?
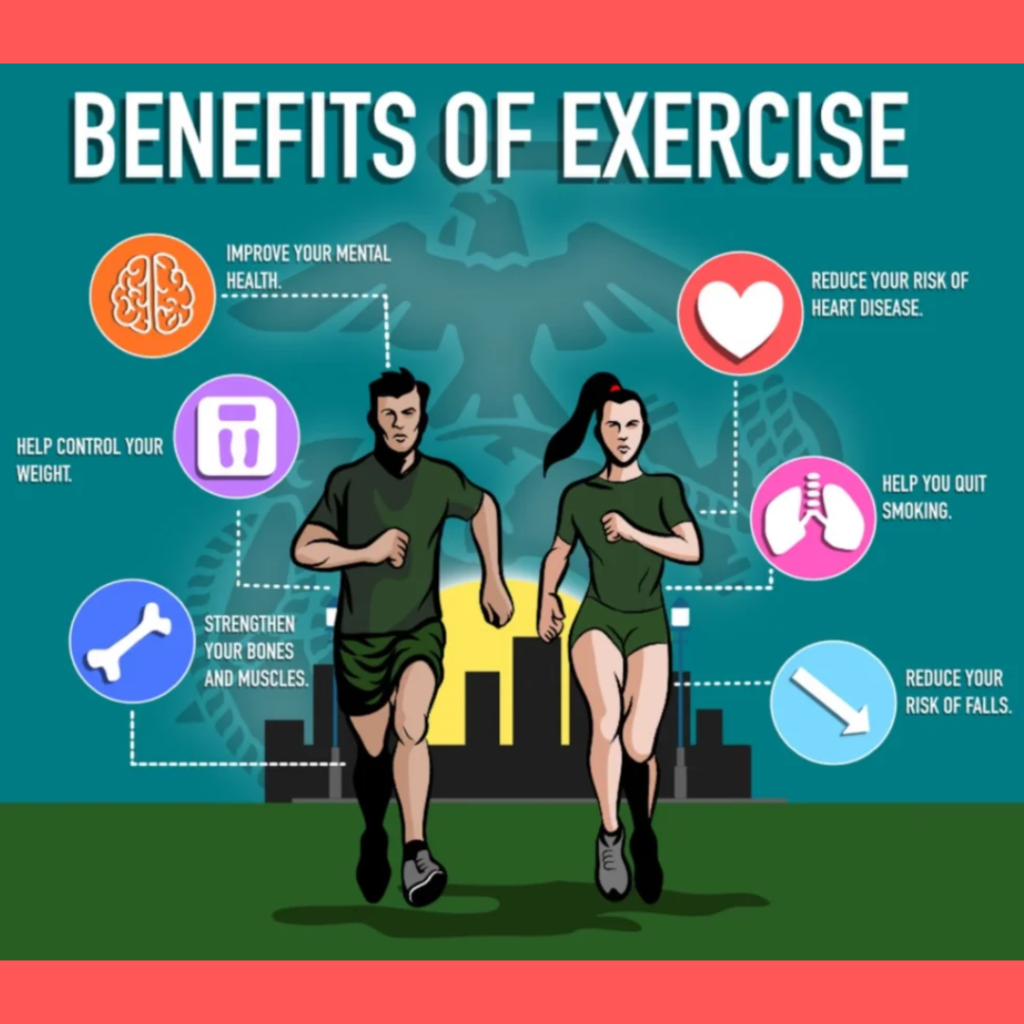
Consistent exercise improves the heart’s efficiency. However, recent studies indicate that various types of physical activity affect the heart in slightly different ways. While all forms of exercise increase the size of the heart, notable differences exist between endurance athletes, like rowers, and strength athletes, like soccer players.
Endurance athletes tend to have hearts with enlarged right and left ventricles, whereas strength athletes often experience a thickening of their heart walls, especially in the left ventricle.
How Does Exercise Affect Lung Health?
While the heart gradually becomes stronger with regular exercise, the respiratory system doesn’t adapt as significantly. The size of the lungs remains the same, but they become more efficient at utilizing oxygen.
Overall, exercise helps the body improve its ability to absorb, circulate, and use oxygen. This enhancement boosts endurance and contributes to better overall health over time.
Health Advantages of Cardiorespiratory Fitness
Improving cardiorespiratory fitness can lower the risk of developing conditions such as:
- Stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Muscular Endurance
Physical fitness also involves muscular endurance, which is the capability of muscles to keep exerting force without getting tired. Strength training leads to larger muscles. In contrast, endurance training doesn’t necessarily increase muscle size.
It is because your body prioritizes the cardiovascular system, ensuring muscles obtain the oxygen-rich blood they need to keep working. When training for endurance, a key change in muscles involves the two types of muscle fibers: slow twitch and fast twitch. Fast twitch fibers get tired easily and contract rapidly.
They consume lots of energy and are ideal for sprints. These fibers are whitish because they don’t rely on blood to work. Slow twitch fibers excel in endurance activities, as they can perform tasks without fatigue. These fibers are found in core muscles and appear red because they have stores of myoglobin and depend on a rich supply of oxygenated blood.
Different exercises target slow twitch fibers, fast twitch fibers, or both. For instance, sprinters tend to have more fast twitch fibers, while long-distance runners have more slow twitch fibers.
- Muscular Strength
Muscular strength can be assessed in several ways. Typically, lifting a specific weight in a designated position and comparing the outcomes to any provided population is the most effective method.
Generally, regularly and consistently exercising muscles will lead to increased strength. There are many methods to challenge muscles, but any activity that works a muscle to the point of fatigue will gradually build muscle strength.
What Changes Occur In Muscle Structure Due To Exercise?
Muscles are made up of long muscle cells, each containing contractile proteins known as myosin and actin. These proteins provide strength to the muscle. The muscle cells contract together to create what’s known as a power stroke. The overall force generated depends on how many of these units contract simultaneously.
To build muscle, a person needs to exercise regularly and consume enough protein. While scientists don’t completely understand the exact process of muscle growth, the basic principles are clear.
Exercise causes muscle cells to grow and increases the production of myosin and actin. In muscles that aren’t trained, fibers often fire out of sync. However, with training, they learn to fire together, boosting maximum power output.
- Flexibility
Flexibility is the range of motion a joint can achieve. Flexibility is crucial because it enhances the capability to connect movements together fluently and aids in preventing injuries. It varies for each joint and is influenced by various factors, like the tightness of tendons and ligaments.
Engaging in activities that stretch the tendons, joints, and ligaments can improve flexibility. There are several methods to enhance flexibility. Following a daily stretching routine is often the easiest and most effective way to achieve flexibility throughout the entire body.
- Body Fat Composition
Body fat composition assesses the proportions of fat, muscle, water, and bone in a person’s body. An individual can keep the same weight while significantly altering the balance of these components.
For example, someone with a higher muscle ratio may weigh more than another person of the same waist size and height who has less muscle. There are various methods for determining body fat composition.
Concluding Thoughts
Generally, physical fitness can mean different things to different individuals. However, the key takeaway is that engaging in regular exercise benefits an individual’s health. The more you exercise, the better you’ll feel and look. Being physically fit can reduce the risk of death from any cause and from heart-related issues, regardless of body weight.
People who are physically fit with a high BMI have lower rates of cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality compared to those with low fitness levels and a normal BMI. Those who are overweight or obese can enhance their health by becoming more active, even if their body weight doesn’t change.
